Windows File Recovery Tool recovers deleted files
What is surprising here is that Windows File Recovery is a command-line tool, i.e., no user interface. As soon as you launch it, it will display a list of options that come with the tool. It expands beyond NTFS recovery and works with SSD (limited by TRIM) and other storage devices. Here is the complete list of options available with it. Here is the list of things we will discuss in this post:
1] Command Usage
/r – Segment mode (NTFS only, recovery using file record segments)/n
Recovering files from non-NTFS file systems is only supported in signature mode.
2] Types of Recovery Mode
Some of the modes use the MFT file, while others require segments, and the last mode works only on large files.
Default mode: It uses the Master File Table (MFT) to locate lost files. It works well when MFT and file segments are both present.Segment mode: It uses Segments, which carries summaries of file information that NTFS stores in the MFT such as name, date, size, type, and the cluster/allocation unit index.Signature mode: This mode only requires that the data is present and searches for specific file types. You can use this mode to recover files from external devices like USB, memory card, and so on.
3] How to use Windows File Recovery in Windows 10?
Open the File Recovery program from the Start menu. It will instantly launch the command prompt, and UAC will prompt for permission. Once allowed, you should see all the options. Do note that you cannot recover to the same partition. It should be a different partition or even better if you recover it to drive. Here are some examples. Default Mode: Recover a specific file Segment mode (/r): Recover types of file Signature mode examples (/x): When using the signature mode, it’s helpful first to see the supported extension groups and corresponding file types. During the recovery process, you will be asked if you want to overwrite, keep a duplicate, and the options to be used for the future. You can choose to overwrite all, but I would recommend you to have enough storage at the destination and keep all copies. You never know which file is corrupt. Read: How to recover Files lost during Cut and Paste in Windows
4] Which recovery model should you use and when?
5] Which file types are supported in the Signature model?
The tool has a default filter list of extensions such as adm, admx, appx, appx, ascx, asm, aspx, aux, ax, bin, browser. You can enable them by using the /e switch.
6] Recovery Logic used by Windows File Recovery
The recovery logic used here is the same as used by other recovery programs. The mode uses Master File Tabel to find records of the deleted files along with File Record Segment. There is an additional copy of MFT which comes in handy to find the exact physical location of the deleted files.
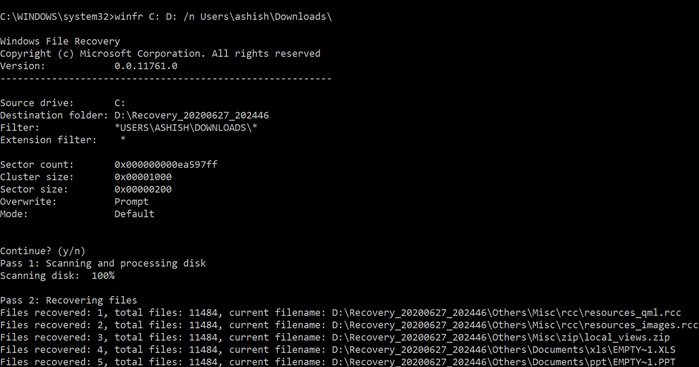
Here is the result of a recovery made through Windows File Recovery tool.
Not all the files were useful, but many were. It is not surprising as a lot depends on how much of the storage space was physically overwritten. While the tool is promising, it still needs a user interface and has its limitations. You can download it from the Microsoft Store. TIP: WinfrGUI is a free tool that adds a graphical user interface to Windows File Recovery. This makes it more accessible to folks who do not use the command prompt.