Enable Windows to Soft Disconnect a computer from a Network
When the setting is enabled, Windows will soft-disconnect a computer from a network – not immediately or abruptly though. As opposed to this, if the setting is disabled, Windows will disconnect a computer or a PC from a network immediately. You have two ways to configure Soft Disconnect a computer from a Network in Windows 10: Please note that if the setting is not configured, the default behavior is soft-disconnect.
1] Tweaking the Registry Setting
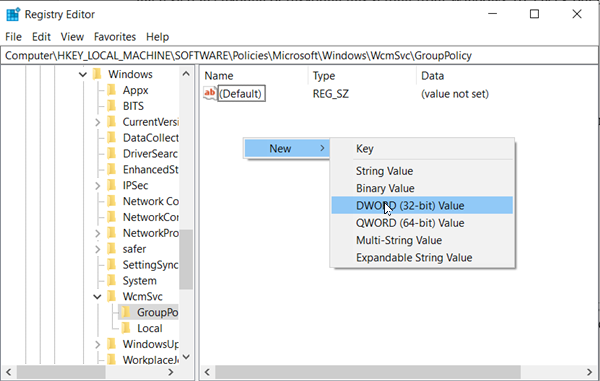
Press Win+R in combination to bring up the ‘Run’ dialog box. In the empty field of the box, type ‘regedit’ and hit the ‘Enter’ key. When the Registry Editor opens, navigate to the following path address – If you do find such entry then, create it.
Now, create a new 32-bit DWORD value SoftDisconnectConnections and configure its value as follows:
0 = Disable Soft Disconnect1 = Enable Soft Disconnect
You can simply choose to delete the SoftDisconnectConnections value to restore the system defaults. When done, close the Registry Editor and restart your computer to allow the changes to take effect.
2] Changing the Group Policy Setting
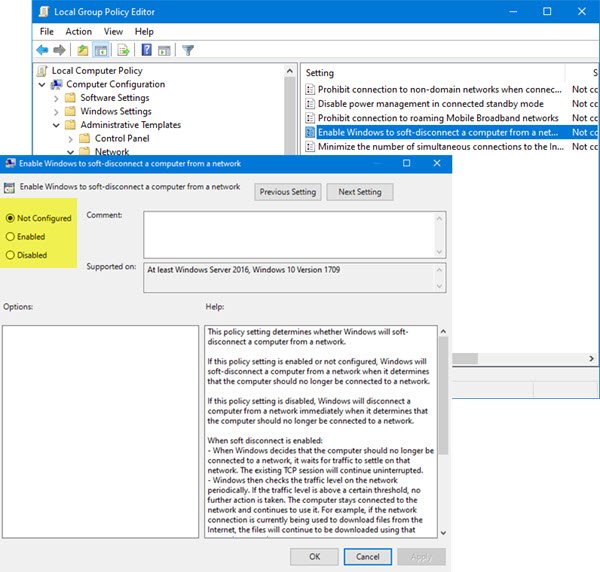
Press Win+R in combination to bring up the ‘Run’ dialog box. In the empty field of the box, type ‘gpedit.msc’ and hit the ‘Enter’ key Now, when the Local Group Policy editor app opens, or launch it for all users except Administrator, or for a specific user. Next, navigate to the following folder: Switch to the right-pane and double-click on the ‘Enable Windows to soft-disconnect a computer from a network’ option.
Set the policy to ‘Disabled’ to disable the feature. If this policy setting is enabled or not configured, Windows will soft-disconnect a computer from a network when it determines that the computer should no longer be connected to a network. If this policy setting is disabled, Windows will disconnect a computer from a network immediately when it determines that the computer should no longer be connected to a network. When soft disconnect is enabled:
When Windows decides that the computer should no longer be connected to a network, it waits for traffic to settle on that network. The existing TCP session will continue uninterrupted.Windows then checks the traffic level on the network periodically. If the traffic level is above a certain threshold, no further action is taken. The computer stays connected to the network and continues to use it. For example, if the network connection is currently being used to download files from the Internet, the files will continue to be downloaded using that network connection.When the network traffic drops below this threshold, the computer will be disconnected from the network. Apps that keep a network connection active even when they’re not actively using it (for example, email apps) might lose their connection. If this happens, these apps should re-establish their connection over a different network.
This policy setting depends on other group policy settings. For example, if ‘Minimize the number of simultaneous connections to the Internet or a Windows Domain’ is disabled, Windows will not disconnect from any networks. You can also leave it as Not configured or set it to ‘Enabled’. That’s all!